華語音韻捜尋系統 CPSS
When you want to:
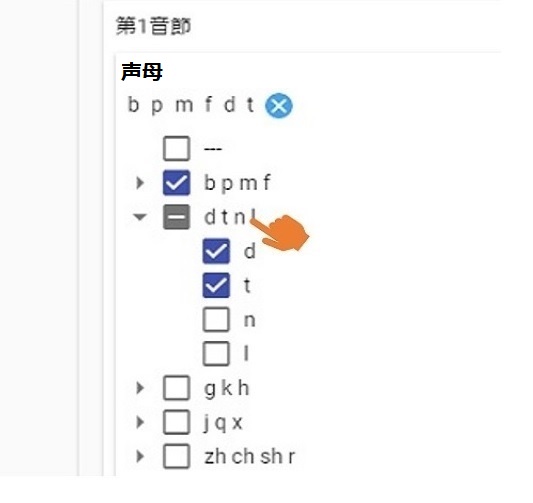
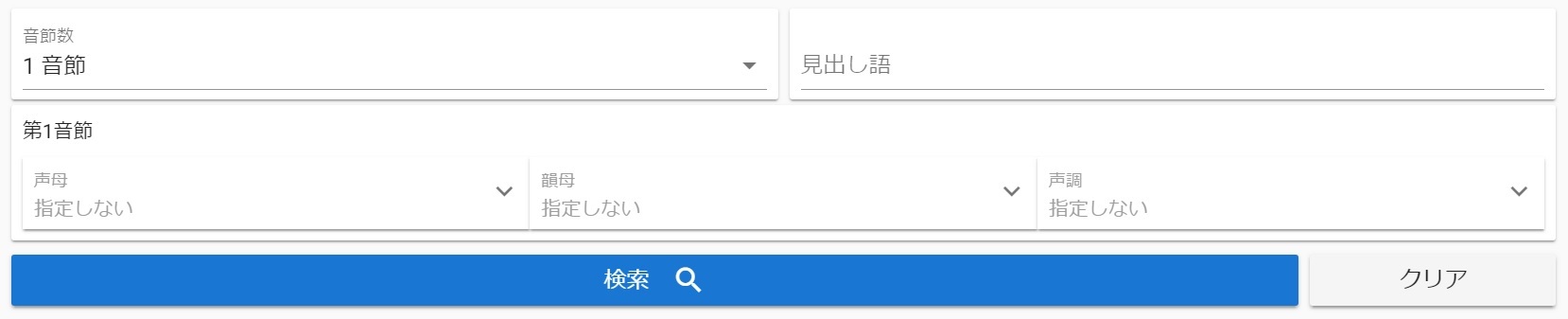
- Make a practice test with two-syllable words which differ only in aspiration
- Find several Chinese words in which the first syllable ends in /n/ and the second syllable ends in /ŋ/
- Practice the pronunciation of word that contain more than one Second tone in a row
CPSS would give you a right answer no matter how complicated your need for phonetic conditions is.
CPSS has about 4000 words and idioms that are frequently used at Levels 4 and 3 of the Chinese Proficiency Test (中国語検定試験). CPSS also has more than 100 Japanese proper nouns such as common surnames and province/region names. These nouns whould be helpful for beginners to introduce themselves in the classroom.

 .
.